Is the cautious mood of optimism an accurate representation of where the economy and construction sector is heading in Cambodia, driven by large-scale infrastructure projects and an increasingly broadening range of foreign direct investment?
Cambodia Moving In The Right Economic Direction
The National Bank of Cambodia (NBC), has predicted Cambodia’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to grow by six per cent in 2024, while the decline in inflation will help the economic conditions of the Kingdom.
NBC Governor Chea Serey, who has been busy signing a number of agreements with other central banks to help facilitate cross-border payments, said in May 2024 that, “ Cambodia’s economy is supported mainly by exports, both garment and non-garment products, increasing of the tourism sector and related sectors, while agricultural sector grows at a slower pack,” at the launch of the Financial Stability Review 2023.
Another factor that the Cambodian government has been saying unanimously is the impact of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and other Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) which should drive increased foreign direct investment- crucial to the economic growth and investment into ky projects designed to better place Cambodia as a logistics hub in the region as well as allowing it to diversify its productions and exports.
Cambodian Structural Reforms
In addition, according to the National Strategic Budget Plan for 2025, structural and systemic reforms aimed at strengthening economic and social resilience include:
- Development of human capital through strengthening the quality of education, sports, science, technology, and technical skills training.
- Economic diversification and increasing competitiveness through the development of key and new sources of economic growth; promoting the energy, water, and digital sectors; and improving the business and investment environment.
- Private sector and employment development through labour market development; promoting small and medium enterprises and new businesses; strengthening competition; and market economy mechanisms.
- Sustainable, sustainable, and environmental development through strengthening resilience, natural resource management, culture and tourism, agricultural promotion, and climate change.
- Digital economic and social development through the building of digital governments and citizens; digital business development; building and developing digital infrastructure; and developing financial technology.

Attracting International Investments - Forging New Logistics Avenues
Cambodia has embarked on an ambitious infrastructure development drive, with a focus on transforming its transportation and logistics network over the next decade. The government previously unveiled its 174-project master plan, requiring an investment of approximately USD $36.6 billion, to achieve its goal of becoming an upper-middle-income country by 2030 and a high-income nation by 2050.
The Comprehensive Master Plan includes 94 road, eight railway, 23 waterway, 20 sea, and 10 air transport projects, as well as 15 logistics and four other infrastructure development ventures - a long-term strategy to interconnect all modes of transportation and link them with logistics centres in the Kingdom.
Connecting The Kingdom’s Road, Air & Sea

The master plan includes the construction of expressways, high-speed rail lines, and other significant infrastructure projects such as airports and ports - and most notably and contentiously - the Funan Techo Canal.
The government is seeking assistance from foreign allies, particularly investment from China, Korea and Japan, but it's also western nations who will be looking to add their engineering expertise based on the number of UK, French, Australian and US delegations and business meetings which have been taking place over the past 18 months.
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has led the infrastructure charge, with major projects such as Cambodia's first expressway connecting Phnom Penh and Sihanoukville proving to be a success and two more are under development.
Japan has focused on a range of projects, including wastewater treatment facilities and road upgrades as well as the Sihanoukville Autonomous Port - currently the only deep-water seaport in the Kingdom. The Japanese have also completed urban transport and rail feasibility studies in Phnom Penh.
The expansion of the international deep-sea port of Sihanoukville, which handles about 60 per cent of Cambodia's import and export traffic, is their most notable project. The port expansion, estimated to cost around USD $750 million, aims to alleviate congestion that has increased over the past decade due to rapid economic growth.
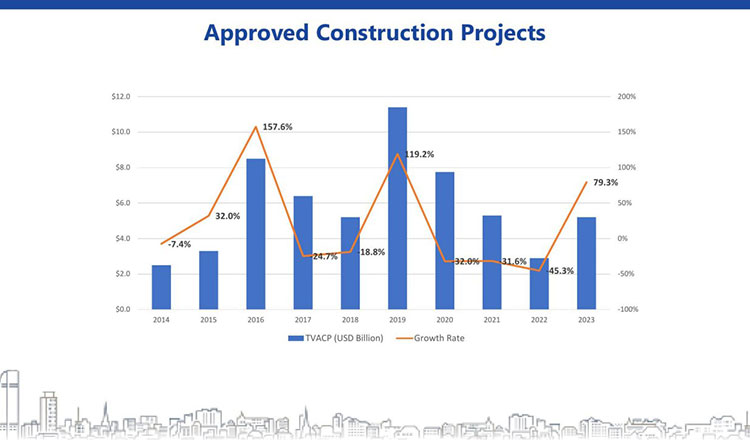
The Cambodian construction industry has wavered but FDI and continued expansion of major infrastructure should assist its rebound in 2024 as major road, rail, port, and airport projects continue to attract foreign interest.

Foreign direct investment from Asian partners remains the main source of funding for transport and energy projects but social infrastructure, such as schools and hospitals, will also benefit from regional development funding, while the accelerated influx of tourists and manufacturing (especially with beneficial trade deals and more special economic zones being investigated) might spur private investment in the non-residential building segment.
The government's efforts to modernise and upgrade infrastructure and logistics systems present an important opportunity for private-sector investment and private-public partnerships. The latest of which is the on-again-and-off-again Kampot International Tourism Port which is now expected to have a private partner appointed before the end of the year and have that port operational by the year’s end too.
Urban areas will also benefit from the Urban Infrastructure Development Project funded by the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) which is supporting the Government of the Kingdom of Cambodia in providing basic urban services such as water supply, sanitation, drainage, and solid waste management and access to climate and disaster-resilient urban infrastructure in participating towns in Cambodia.
Improved Construction Sector
There are also systematic improvements being planned to make the construction sector more eco-friendly, updated construction laws and practises are due to be introduced and the Ministry of Land Management, Urban Planning and Construction (MLMUPC) confirmed the national land registry records of all Cambodian land titles will be recorded and digitized to improve efficiency.
The Cambodia Green Building Council (CamGBC) will also develop a green building certification tool for the Cambodian construction sector.
If 2024-2025 are to see a revival for the construction industry in Cambodia, driven by large-scale infrastructure development and an expanding middle class, there will be increasing demand for quality housing and commercial projects.




Comments